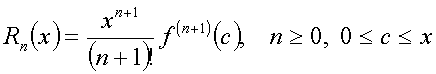|
0
0.0083333 0.016667 0.26667
Q2. Given f(3)=6, f'(3)=8, and f''(3)=11, and that all other higher order derivatives of f(x) are zero at x=3, and assuming the function and all its derivatives exist and are continuous between x=3 and x=7, the value of f(7) is 38.000 79.500 126.00 331.50
Q3. Given that y(x) is the solution to dy/dx=y3+2, y(0)=3, the value of y(0.2) from a second order Taylor polynomial is 4.400 8.800 24.46 29.00
Q4. The series

is a Maclaurin series for the following function cos(x) cos(2x) sin(x) sin(2x) Q5. The function is called the error function. It is used in the field of probability and cannot be calculated exactly for finite values of x. However, one can expand the integrand as a Taylor polynomial and conduct integration. The approximate value of erf(2.0) using first three terms of the Taylor series around t=0 is -0.75225 0.99532 1.5330 2.8586
Q6. Using the remainder of Maclaurin polynomial of nth order for f(x) defined as the least order of the Maclaurin polynomial required to get an absolute true error of at most 10-6 in the calculation of sin(0.1) is (do not use the exact value of sin(0.1) or cos(0.1) to find the answer, but the knowledge that |sin(x)| ≤1 and |cos(x)|≤1).3 5 7 9
|