|
Q1. The goal of forward elimination steps
in the Na´ve Gauss elimination method is to reduce the coefficient matrix to
a (an) _____________ matrix.
diagonal
identity
lower triangular
upper triangular
Q2.
Division by zero during forward elimination steps in Na´ve Gaussian
elimination of the set of equations [A][X]=[C] implies the coefficient
matrix [A] is
invertible
nonsingular
not
determinable to be singular or nonsingular
singular
Q3.
Using a computer with four significant digits with chopping, Na´ve Gauss
elimination solution to
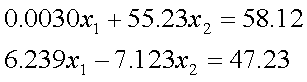
is
x1
= 26.66; x2 = 1.051
x1
= 8.769; x2 = 1.051
x1
= 8.800; x2 = 1.000
x1
= 8.771; x2 = 1.052
Q4.
Using a computer with four significant digits with chopping, Gaussian
elimination with partial pivoting solution to
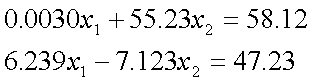
is
x1
= 26.66; x2 = 1.051
x1
= 8.769; x2 = 1.051
x1
= 8.800; x2 = 1.000
x1
= 8.771; x2 = 1.052
Q5. At
the end of forward elimination steps of Na´ve Gauss Elimination method
on the following equations
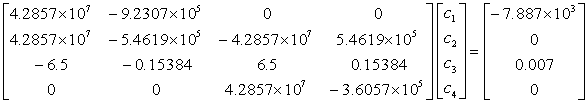
the
resulting equations in the matrix form are given by
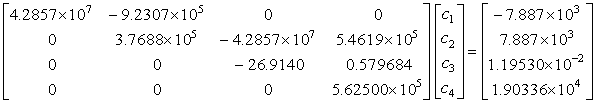
The
determinant of the original coefficient matrix is
0.00
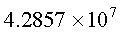
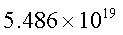
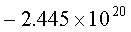
Q6. The following data is given for the
velocity of the rocket as a function of time. To find the velocity at
t=21 s, you are asked to use a quadratic polynomial, v(t)=at2+bt+c
to approximate the velocity profile.
|
t |
(s) |
0 |
14 |
15 |
20 |
30 |
35 |
|
v(t) |
m/s |
0 |
227.04 |
362.78 |
517.35 |
602.97 |
901.67 |
The correct set of equations that will find a, b and c
are
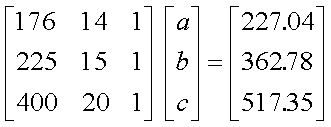
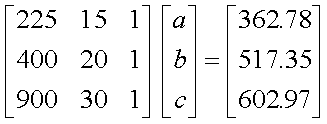
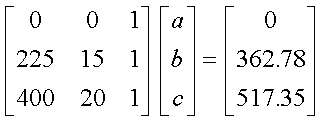
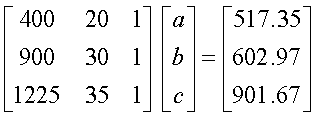
|