|
Q1.
A square matrix [A]nxn
is diagonally dominant if
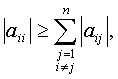 i = 1, 2, …, n
i = 1, 2, …, n
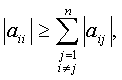 i
= 1, 2, …, n and i
= 1, 2, …, n and
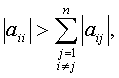 for
any i = 1, 2, …, n for
any i = 1, 2, …, n
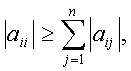 i
= 1, 2, …, n and i
= 1, 2, …, n and
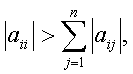 for
any i = 1, 2, …, n for
any i = 1, 2, …, n
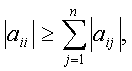 i
= 1, 2, …, n i
= 1, 2, …, n
Q2.
Using [x1 x2 x3]
= [1 3 5] as the initial guess, the value of [x1
x2 x3] after three iterations
of Gauss-Seidal method is
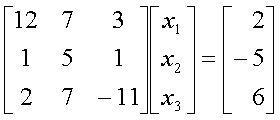
[-2.8333
-1.4333 -1.9727]
[1.4959
-0.90464 -0.84914]
[0.90666
-1.0115 -1.0242]
[1.2148
-0.72060 -0.82451]
Q3.
To ensure that the following system of equations,
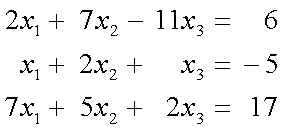
converges using the Gauss-Siedal method, one
can rewrite the above equations as follows:
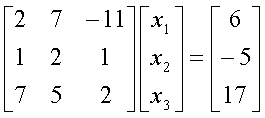
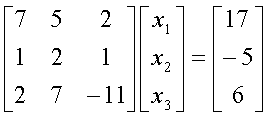
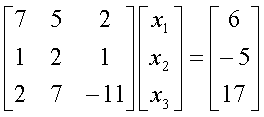
The
equations cannot be rewritten in a form to ensure convergence.
Q4.
For
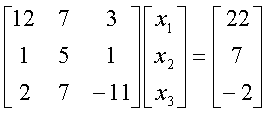
and
using 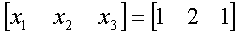 as
the initial guess, the values of as
the initial guess, the values of 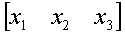 are
found at the end of each iteration as are
found at the end of each iteration as
|
Iteration # |
x1 |
x2 |
x3 |
|
1 |
0.41666 |
1.1166 |
0.96818 |
|
2 |
0.93989 |
1.0183 |
1.0007 |
|
3 |
0.98908 |
1.0020 |
0.99930 |
|
4 |
0.99898 |
1.0003 |
1.0000 |
At
what first iteration number would you trust at least 1 significant digit
in your solution?
1
2
3
4
Q5.
The algorithm for the
Gauss-Seidal method to solve [A] [X] = [C] is given as follows when using nmax iterations. The initial value of [X] is stored in [X].
Sub
Seidal(n, a, x, rhs, nmax)
For k = 1 To nmax
For i = 1 To n
For j = 1 To n
If (i <> j) Then
Sum = Sum + a(i, j) * x(j)
endif
Next j
x(i) = (rhs(i) - Sum) /
a(i, i)
Next i
Next k
End Sub
Sub
Seidal(n, a, x, rhs, nmax)
For k = 1 To nmax
For i = 1 To n
Sum = 0
For j = 1 To n
If (i <> j) Then
Sum = Sum + a(i, j) * x(j)
endif
Next j
x(i) = (rhs(i) - Sum) / a(i, i)
Next i
Next k
End Sub
Sub Seidal(n, a, x, rhs, nmax)
For k = 1 To nmax
For i = 1 To n
Sum = 0
For j = 1 To n
Sum = Sum + a(i, j) * x(j)
Next j
x(i) = (rhs(i) - Sum) / a(i, i)
Next i
Next k
End Sub
Sub Seidal(n, a, x, rhs, nmax)
For k = 1 To nmax
For i = 1 To n
Sum = 0
For j = 1 To n
If (i <> j) Then
Sum = Sum + a(i, j) * x(j)
endif
Next j
x(i) = rhs(i) / a(i, i)
Next i
Next k
End Sub
Q6. Thermistors measure temperature, have a
nonlinear output and are valued for a limited range. So when a thermistor is manufactured, the manufacturer supplies a resistance vs.
temperature curve. An accurate representation of the curve is generally
given by
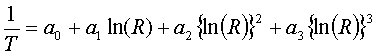
where T is temperature in Kelvin,
R is
resistance in ohms, and 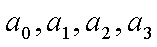 are
constants of the calibration curve. are
constants of the calibration curve.
Given the following for a thermistor
|
R |
T |
|
ohm |
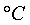 |
|
1101.0
911.3
636.0
451.1 |
25.113
40.120
50.128 |
the value of temperature in
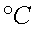 for
a measured resistance of 900 ohms most nearly is for
a measured resistance of 900 ohms most nearly is
30.002
30.472
31.272
31.445
|