|
Q1. The exact solution to the boundary value
problem
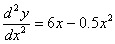 ,
and ,
and 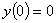 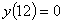
for
y(4) is
-234.67
0.0000
16.000
37.333
Q2. Given
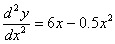 , ,
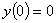 , ,
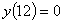 , ,
the value of 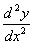 at
y(4) using
the finite difference method and a step size of h=4 can
be approximated by at
y(4) using
the finite difference method and a step size of h=4 can
be approximated by
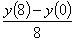
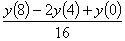
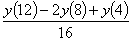
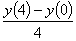
Q3. Given
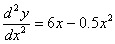 , ,
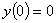 , ,
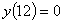 , ,
The value of y(4) using
the finite difference method with a second order accurate central divided
difference method and a step size of h=4 is
0.000
37.333
-234.67
-256.00
Q4. The transverse deflection u of a cable of length, L,
that is fixed at both ends, is given as a solution to
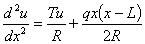
where
T =
tension in cable
R =
flexural stiffness
q =
distributed transverse load
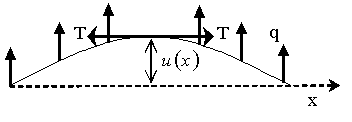
Given L=50", T=200 lbs, q=75lbs/in,
R=75x106 lbs-in2, using finite difference method modeling
with second order central divided difference accuracy and a step size of
h=12.5",
the value of the deflection at the center of the cable
most nearly is
0.072737"
0.08832"
0.081380"
0.084843"
Q5. The radial displacement, u
of a
pressurized hollow thick cylinder (inner radius=5″, outer radius=8″) is
given at different radial locations.
|
Radius |
Radial Displacement |
|
(in) |
(in) |
|
5.0 |
0.0038731 |
|
5.6 |
0.0036165 |
|
6.2 |
0.0034222 |
|
6.8 |
0.0032743 |
|
7.4 |
0.0031618 |
|
8.0 |
0.0030769 |
The maximum normal stress, in psi, on the
cylinder is given by
  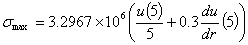
The maximum stress, in psi, with second
order accuracy is
Hint:
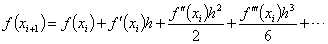 ,
and ,
and
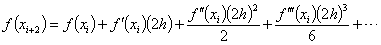
where
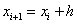
2079.3
2104.5
2130.7
2182.0
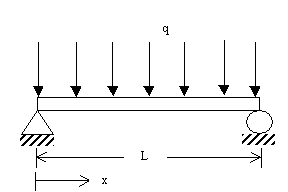
Q6. For a simply supported beam (at
x=0 and x=L)
with a uniform load q, the vertical deflection v(x) is
described by the boundary value ordinary differential equation as
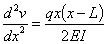 , ,
where
E = Young’s modulus of
elasticity of beam
I = second moment of area.
This ordinary differential equation is
based on assuming that dv/dx is
small. If dv/dx is
not small, then the ordinary differential equation is given by
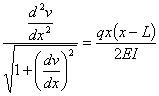
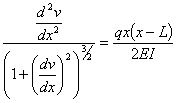
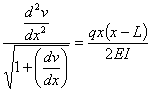
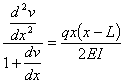
Complete Solution
Multiple choice questions on other topics
|
