|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pick the most
appropriate answer. |
|
Q1. To solve the ordinary
differential equation
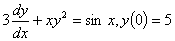 , ,
by Runge-Kutta 4th
order method, you need to rewrite the equation as
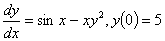
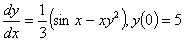
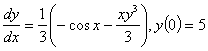
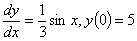
Q2. Given
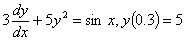 and
using a step size of and
using a step size of
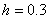 ,
the value of ,
the value of
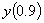 using
Runge-Kutta 4th order method is most nearly using
Runge-Kutta 4th order method is most nearly
-
0.25011
-4297.4
-1261.5
0.88498
Note: At the end of this
document, see formulas used to answer this question as there are a few
different versions of the Runge-Kutta 4th order method.
Q3. Given
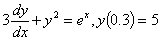 ,
and using a step size of ,
and using a step size of
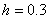 ,
the best estimate of ,
the best estimate of
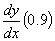
Runge-Kutta
4th order method is most nearly
-1.6604
-1.1785
-0.45831
2.7270
Note: At the end
of this document, see formulas used to answer this question as there are
a few different versions of the Runge-Kutta 4th order method.
Q4. The velocity (m/s) of
a parachutist is given as a function of time (seconds) by
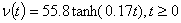
Using
Runge-Kutta 4th order method with a step size of 5 seconds,
the distance traveled by the body from
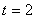 to to
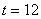 seconds
is estimated most nearly as seconds
is estimated most nearly as
341.43
m
428.97
m
429.05
m
703.50
m
Note: At the end of this document, see formulas used to answer this
question as there are a few different versions of the Runge-Kutta 4th
order method.
Q5. Runge-Kutta
method can be derived from using first three terms of Taylor series of
writing the value of
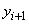 ,
that is the value of ,
that is the value of
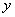 at at
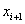 ,
in terms of ,
in terms of
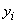 and
all the derivatives of and
all the derivatives of
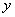 at at
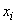 .
If .
If 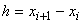 ,
the explicit expression for ,
the explicit expression for
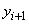 if
the first five terms of the Taylor series are chosen for the ordinary
differential equation if
the first five terms of the Taylor series are chosen for the ordinary
differential equation
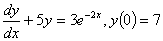 , ,
would be
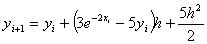
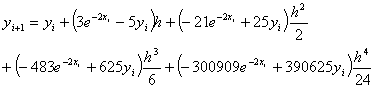
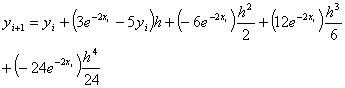
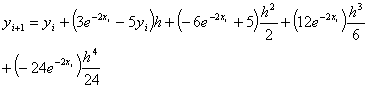
Q6. A hot solid
cylinder is immersed in an cool oil bath as part of a quenching process.
This process makes the temperature of the cylinder,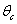 ,
and the bath, ,
and the bath,
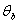 ,
change with time. If the initial temperature of the bar and the oil
bath is given as 600°
C and 27°C,
respectively, and ,
change with time. If the initial temperature of the bar and the oil
bath is given as 600°
C and 27°C,
respectively, and
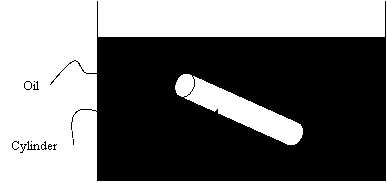
Length of cylinder = 30 cm
Radius of cylinder = 3 cm
Density of cylinder = 2700 kg/m^3
Specific heat of cylinder = 895 J/kg-K
Convection heat transfer coefficient = 100 W/(m^2-K)
Specific heat of oil = 1910 J/(kg-K)
Mass of oil = 2 kg
The coupled ordinary differential equations governing the heat transfer are given by
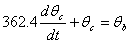
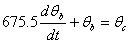
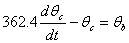
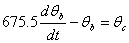
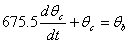
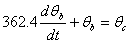
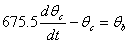
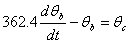
The following
equations are used to answer questions#2, 3, and 4
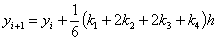
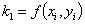
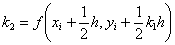
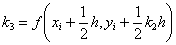
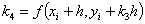
Complete Solution
Multiple choice questions on other topics
|
